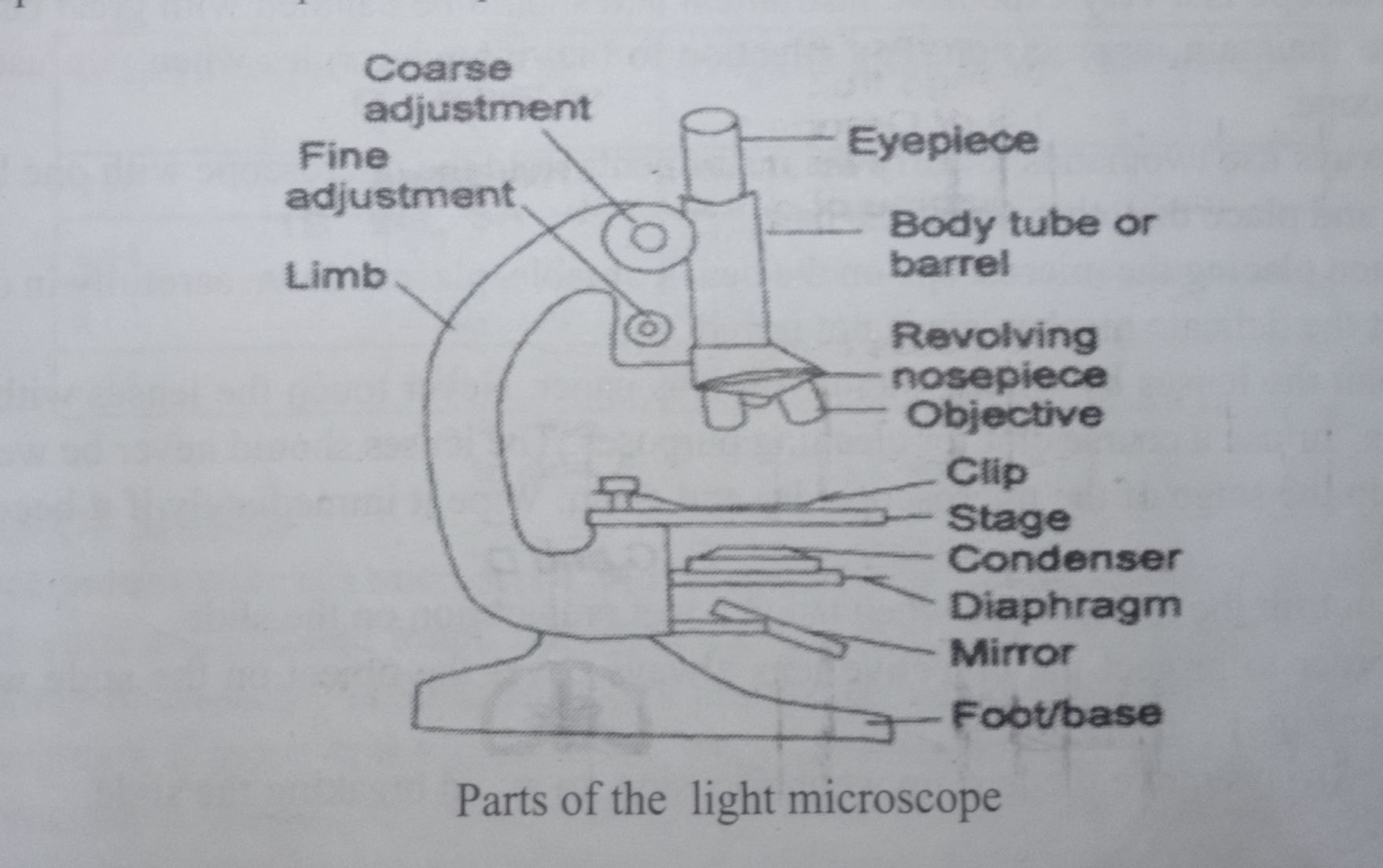

A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye and also to separate minute details. The ability of a microscope to distinguish two very close objects as being separated from each other is its resolution or resolving power.
The science of investigating small objects using a microscope is called microscopy. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
Microscopes can be separated into several different classes. One grouping is based on what interacts with the sample to generate the image, i.e., light (optical microscopes) or electrons (electron microscopes).
| Light/Optical microscope | Electron microscope |
|---|---|
| Have a less resolving power | Have a greater resolving power |
| Uses photons or light energy | Uses electrons |
| Have longer wavelengths that allow less magnification | Have shorter wavelengths that allow greater magnification |
| Uses a simple lens | Uses an electrostatic or electromagnetic lens |
| Uses human eye | Uses fluorescent screen or electron detector |
| Uses objective lens | Magnetic objective |
| Uses eyepiece or projector lenses | Electromagnet or magnetic projector |
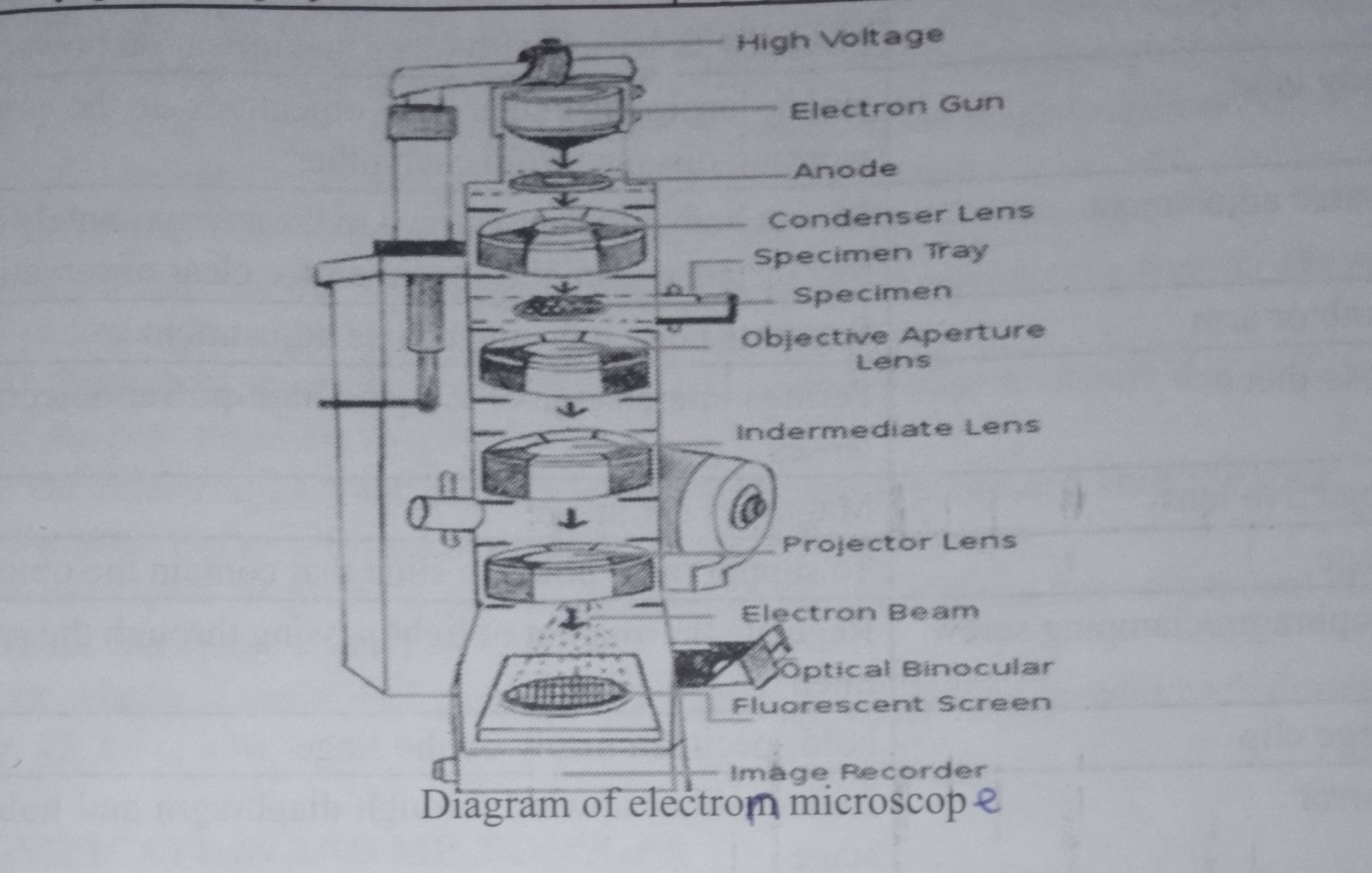
The advantage of using the electron microscope is that electron microscopes (EM) have a greater resolving power than a light-powered optical microscope.
The advantage of using the optical microscopes is that it can be used to view live specimen whilst the electron microscope can only be used to view dead specimen.
Also the optical microscope is cheaper but electron microscope is expensive.